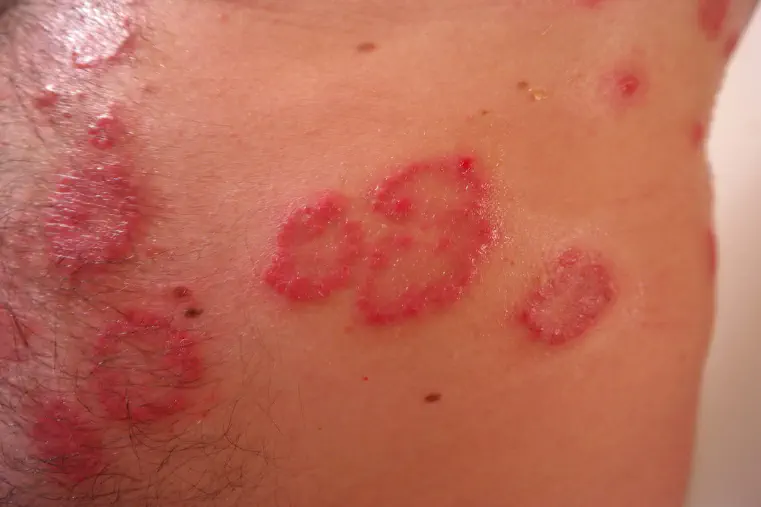
Are you one of the many people who have ever experienced those pesky red patches on your skin?
These patches of redness on skin can be uncomfortable and concerning, but the good news is that there are ways to both prevent and treat them.
Understanding the causes and treatments of these red patches is essential in maintaining healthy skin.
In this piece, we’ll explore what patches of redness on skin are, why it’s important to understand them, and what we’ll cover in this comprehensive guide.
So, whether you’re experiencing these symptoms for the first time or you’re looking for ways to manage them, read on to learn more.
Causes of patches of redness on skin
Patches of redness on skin can be caused by a variety of factors, from allergies and irritants to infections and autoimmune diseases.
Allergies and irritants such as cosmetics, soaps, and fabrics can cause redness on the skin. These irritants can cause a reaction on the skin that leads to redness, itching, and inflammation.
Infections such as fungal infections, bacterial infections, and viral infections can also lead to patches of redness on the skin.
Fungal infections like ringworm can cause circular red patches on the skin, while bacterial infections like cellulitis can cause a red and swollen area on the skin.
Viral infections like shingles can cause redness and a painful rash on the skin.
Skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea are also common causes of patches of redness on the skin.
These conditions can cause chronic inflammation, which can lead to redness, itching, and flaking.
Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can also cause redness on the skin.
Finally, environmental factors such as exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, and pollution can also cause redness on the skin.
It’s important to understand the different causes of redness on the skin so that proper treatment can be administered.
Allergies and irritants
Allergies and irritants are common causes of patches of redness on skin. An allergy is an immune response to a substance that is not normally harmful to the body, while an irritant is a substance that directly causes irritation or damage to the skin.
Common examples of allergens and irritants include cosmetics, fragrances, soaps, detergents, metals, and certain fabrics.
When the skin is exposed to an allergen or irritant, it can cause a reaction that leads to redness, itching, and inflammation. This is because the immune system sends out chemicals to fight off the perceived threat, which can cause an allergic or irritant contact dermatitis.
Prevention tips for allergies and irritants include avoiding exposure to known allergens and irritants, using hypoallergenic products, and wearing protective clothing when necessary.
Treatment options for redness caused by allergies and irritants include over-the-counter topical creams, such as hydrocortisone, which can help to reduce inflammation and itching.
In severe cases, prescription medications, such as corticosteroids or antihistamines, may be necessary.
It’s important to identify and avoid allergens and irritants to prevent further episodes of redness on the skin caused by these factors.
Infections
Infections are another common cause of patches of redness on skin. Infections can be caused by fungi, bacteria, and viruses.
Fungal infections, such as ringworm, can cause circular red patches on the skin, while bacterial infections like cellulitis can cause a red and swollen area on the skin.
Viral infections like shingles can cause redness and a painful rash on the skin. Infections occur when microorganisms invade the skin and cause an immune response. This can lead to redness, swelling, and inflammation.
Prevention tips for infections include practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with people who have an infectious disease, and avoiding exposure to contaminated objects and surfaces.
Treatment options for redness caused by infections vary depending on the type of infection. Antifungal medications are used to treat fungal infections, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, and antiviral medications are used to treat viral infections. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
It’s important to seek treatment for infections as soon as possible to prevent the spread of the infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Skin conditions
Skin conditions are a broad category of disorders that can cause patches of redness on the skin.
Some common examples of skin conditions include eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, and lupus.
Skin conditions can be caused by genetic factors, environmental factors, or a combination of both. When the skin is affected by a skin condition, it can become inflamed, itchy, and red.
In some cases, the patches of redness can be accompanied by flaking, scaling, or oozing.
Prevention tips for skin conditions depend on the specific condition but may include avoiding triggers, such as certain foods or environmental factors.
Treatment options for skin conditions vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Over-the-counter creams and ointments, such as corticosteroids or antihistamines, can be used to reduce inflammation and itching.
In more severe cases, prescription medications, such as immunosuppressants or biologic agents, may be necessary. It’s important to work with a dermatologist to identify the underlying cause of the skin condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
Some examples of autoimmune diseases that can cause patches of redness on the skin include lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma.
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly targets the skin, resulting in patches of redness, swelling, and inflammation. In some cases, the patches of redness may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as joint pain or fatigue.
Prevention tips for autoimmune diseases are not well-established, as the underlying causes of these conditions are not fully understood. However, living a healthy lifestyle, such as getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking, may help reduce the risk of developing autoimmune diseases.
Treatment options for autoimmune diseases vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Medications, such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic agents, can be used to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease.
In some cases, lifestyle changes and complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or massage therapy, may also be helpful in managing symptoms. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan for autoimmune diseases.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors can play a role in causing patches of redness on the skin.
Some examples of environmental factors that can contribute to skin redness include exposure to extreme temperatures, pollution, and UV radiation from the sun.
In some cases, chemicals in household products or cosmetics can also irritate the skin and cause redness. When the skin is exposed to environmental factors, it can become inflamed and irritated, resulting in patches of redness, itching, and flaking.
Prevention tips for environmental factors include avoiding direct exposure to the sun during peak hours, using protective clothing, and avoiding irritants, such as harsh chemicals and fragrances. It’s also important to maintain good skin hygiene and use gentle, fragrance-free products to reduce the risk of skin irritation.
Treatment options for environmental factors depend on the severity of the skin reaction. Over-the-counter creams and ointments can be used to soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
In more severe cases, prescription medications, such as corticosteroids, may be necessary to control the symptoms.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen despite at-home remedies.
Diagnosis of patches of redness on skin
If you experience patches of redness on your skin, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Your healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination to assess the affected areas.
They may ask questions about your symptoms, such as when they first appeared, if they have worsened or improved, and if you have tried any treatments at home.
Diagnostic tests, such as skin cultures or blood tests, may be ordered to help identify the cause of the redness.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist or allergist, for further evaluation and treatment.
It’s important to keep in mind that some causes of skin redness, such as autoimmune diseases, may require long-term management and monitoring. With a proper diagnosis, appropriate treatment can be prescribed to help manage and alleviate symptoms.
Treatment of patches of redness on skin
Treatment for patches of redness on skin varies depending on the underlying cause.
General treatment options may include keeping the affected area clean and dry, avoiding harsh chemicals or irritants, and applying cool compresses or moisturizers to soothe the skin. Topical treatments are often used to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation.
These may include creams or ointments containing corticosteroids, immunomodulators, or antibiotics.
Oral medications, such as antihistamines, antibiotics, or immune-suppressants, may be prescribed for more severe or persistent cases.
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing symptoms. This may involve avoiding triggers or irritants that cause flare-ups, using gentle skin care products, and protecting the skin from sun exposure.
In addition, alternative therapies, such as herbal supplements, acupuncture, or relaxation techniques, may be used to complement conventional treatment.
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition, taking into consideration your medical history, symptoms, and personal preferences.
Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, patches of redness on skin can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies and irritants, infections, skin conditions, autoimmune diseases, and environmental factors.
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include general measures, topical or oral medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
It is essential to seek medical attention if you have persistent or worsening symptoms to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early detection and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
While there is no definitive cure for many of these conditions, ongoing research is being conducted to develop new and more effective treatment options.
By taking an active role in managing your skin health and working with your healthcare provider, you can help manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
FAQs
What are some common causes of patches of redness on skin?
Common causes of patches of redness on skin include allergies, irritants, infections, skin conditions, autoimmune diseases, and environmental factors.
How can I tell if my red patches are a sign of a serious condition?
If you notice any new or unusual patches of redness on your skin, it’s important to seek medical attention. While many cases of red patches are harmless and can be treated easily, some can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition such as skin cancer or an autoimmune disorder.
Are there any over-the-counter treatments for patches of redness on skin?
There are some over-the-counter treatments available for mild cases of red patches on skin, such as hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before using any new products on your skin, especially if you have sensitive skin or are prone to allergies.
What kind of doctor should I see for red patches on my skin?
If you have persistent or severe patches of redness on your skin, you should see a dermatologist. They specialize in diagnosing and treating skin conditions and can provide more targeted treatment options.
Can stress cause patches of redness on skin?
Yes, stress can cause patches of redness on the skin. Stress can trigger the release of certain chemicals in the body that can lead to inflammation, including on the skin.
Are there any lifestyle changes I can make to reduce the occurrence of patches of redness on skin?
Yes, there are some lifestyle changes you can make to reduce the occurrence of patches of redness on the skin. This includes avoiding triggers that may cause inflammation, such as certain foods or irritants, managing stress levels, and protecting the skin from excessive sun exposure.
How long does it typically take for patches of redness on skin to go away with treatment?
The time it takes for patches of redness on the skin to go away with treatment can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases may clear up within a few days, while more severe cases may take several weeks or longer to resolve.
Are there any natural remedies for patches of redness on skin?
There are some natural remedies that may help to reduce patches of redness on the skin, such as applying aloe vera or chamomile to the affected area, using oatmeal baths, and drinking herbal teas with anti-inflammatory properties. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any natural remedies.
Can patches of redness on skin be a sign of cancer?
While patches of redness on the skin can be a symptom of certain types of skin cancer, they are more commonly associated with less serious skin conditions. If you are concerned about the possibility of skin cancer, it’s important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.
Is it safe to use makeup on red patches of skin?
It’s generally safe to use makeup on red patches of skin as long as the products are non-irritating and do not worsen the condition. However, it’s important to avoid applying makeup to open sores or areas of broken skin, and to remove makeup before going to bed to allow the skin to breathe and heal.